Intro to Programming Nanodegree
Ongoing
Lesson 1: The Basics
How the Web Works
The web is the group of computers communicating using HTTP requests for HTML documents between web browsers and servers.
[Video]HTML
Hypertext Markup Language is most of what you see on the web. Text is what you see and markup is how it looks.
[Video]Stupid Computers
They interpret instructions literally. The smallest mistakes can break everything. A precise sequence of steps is required.
Inline vs Block Elements
Block elements have an invisible box around them, while inline elements can be anywhere.
Lesson 2: Creating Structured Documents With HTML
HTML-CSS-DOM
HTML and CSS are both languages with syntax and rules. HTML defines the content of the page, while CSS defines the way it is styled. The DOM (Document Object Model) is the convention by which HTML and other markup languages are represented: a tree structure called the DOM tree.
Text Editors
Recommended text editors:
-
Atom (recommended)
- script - run code in atom
- autoclose-html - automatically close HTML tags
- preview-plus - preview code in atom
- Sublime Text
Lesson 3: Adding CSS Style and HTML Structure
CSS
Cascading Style Sheets follow the Most Specific Rule Applied: you go down selectors until you reach the most relevant one.
A selector referencing either an HTML tag, .class, or #id. Then define properties and values to the selector.
Reference the CSS stylesheet in the <head> of the HTML document.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
Boxes
Everything on a webpage is a box. Breaking up sections of the page with div tags allows us to neatly boxify the page.
All boxes are made up of 4 components: the margin, border, padding, and content.
To make handling boxes simpler:
- Set sizes using percentages instead of pixels
-
Set the width of a box to include the
content,padding, andborder.* { box-sizing: border-box; }
Layout
CSS has powerful tools to layout content. You can use flexbox by adding the rule display: flex to the CSS of the container. Flexbox makes it easy to put the container's children beside each other.
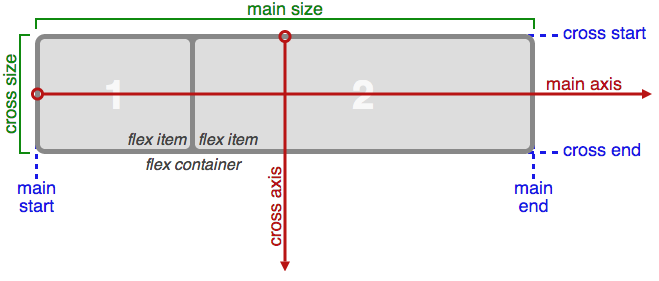
Components of a flex container.
Code, Test, Refine
- Look for natural boxes.
- Look for repeated styles and semantic elements
- Write HTML
- Apply styles (from BIGGEST to smallest)
- Fix things
Use developer tools to test your layout and style.
Command + Alt + i in Chrome on OSX.
Verifying HTML and CSS
Lesson 4: Intro to Serious Programming
The Command Line
The command line is a powerful way to access and control your computer. The most common CLI - command line interface - is the Unix shell. Windows users can use a similar interface by installing git.
This is as opposed to the GUI, the graphical user interface most of us are used to seeing.
Intro to Computer Science
We use a programming language to tell the computer what to do. Python is an example of a high-level language and interpreter that allows the programmer to write in a more human-friendly code to be translated to what the computer needs to execute.
We need programming languages because natural languages have ambiguity and verbosity.
[ Notes from CS101 Unit 1, Python reference]Think Like a Programmer
- Procedural Thinking
- Systems Thinking
- Technological empathy
- Abstract thinking
- Debugging
Grammar
We can use the Backus-Naur Form, invented by John Backus (Fortran), to describe the grammar of the language with simplicity and precision.
<Non-terminal> -> Replacement Expression -> Expression Operator Expression Expression -> Number Operator -> + Operator -> * Number -> 0,1,... Expression -> (Expression)
Lesson 5: Basic Python
Variable & Code Readability
Use variables to represent and describe values. It also allows us to store and reuse important values many times consistently.
To assign a value to a variable:
name = expression
Strings
You can use '', "", or ''' ''' to define a string.
- Concatenation: 'string' + 'string'
- Indexing: 'string'[position]
- Select substring: 'string'[start:end]
- Find: 'string'.find('string', position)
- Replace: 'string'.replace('old', 'new')
- Split: 'string'.split() = ['string', 'string',...]
- Convert: str(Expression) = 'string'
-
Looping:
for c in 'string': Code
Unit 2 Notes, Python Reference 2
Input -> Function -> Output
Also known as procedures or methods, functions allow us to wrap useful code and reuse it consistently. Functions map some input to some output. Procedures affect variables outside the function.
def function(input, argument, parameter):
expression
return output
Remember to always return at the end of a function.
Control Flow
We use if statements to control the flow of the program.
if TestExpression:
Block
elif TestExpression:
Block
else:
Block
Boolean operators take two expressions and return True or False.
< > <= == != or and
Loops
Loops repeat some code until some expression is False.
while TestExpression:
Block
if BreakTest:
break
Code
for name in list: #iterates over list; range(r)
Block
Lesson 6: More Python
Random
We can generate random number by importing
from random import randint randint(start, end)
User Input
x = raw_input('Username:') #python2
x = input('Password:') #python3
main()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print "This only executes when %s is executed rather than imported" % __file__
Use this at the bottom of your program to execute as a script and run tests.
Assignment
When call a function with a parameter, a reference to the object is being passed in. For mutable types, modifying the object with .append() will modify the object outside the function, but using an assignment statement = will not. The exception to this is +=, it will also modify the referenced object.
Lesson 7: Data Structures
Lists
Lists can be a sequence of anything, even other lists. Strings are just a list of characters. String methods apply to lists as well.
list = [['Hello'], 30419, ...] print list[0][0] #>>> 'Hello'
Lists are also mutable, meaning individual components can be changed without the reference changing (which is what happens to strings; a new object is created every time a change is made). Aliasing occurs when there are multiple references to the same object.
p = [1, 2, 4, 8] q = p q[0] = 0 p == q #>>> True
List Operations:
-
list.append(expression)adds element to end of list. -
list + listreturns concatenated list as new object. -
len(list)returns number of child elements. -
list.index(value)returns index of first instance. Returnserrorif list doesn't contain value. -
value in listreturnsTrueif list contains value. ReturnsFalseotherwise. -
value not in list
Dictionary
A dictionary is an unordered list that contains unique keys and their related values. This makes it easy to search for a specific key value rather than going through index positions.
dict = {'index1': 1, 'index2': 10}
dict['awesome'] = True
del dict['index1']
dict
#>>> {'index2': 10, 'awesome': True}
# print every key/value pair
for key, val in dict.items():
print "%s key is associated with %s" % (key, val)
# format using dictionary keys
print """
index2: {index2}
awesome: {awesome}
""".format(**dict)
# safely get value that might not be there
# Default value = None
thing = dict.get('index1')
# get value with a default value
thing = dict.get('index1', "Not found")
Lesson 8: Best Practices
Commenting
- Don't over comment. Use descriptive variable/function names.
- Keep comments up-to-date.
- Be concise.
Documentation
Python (but not all languages) allows you to use a docstring at the beginning of classes, functions, etc.
"""The docstring of a script shoudl be its 'usage' massage. Describe the scripts's function, command line syntax, environment variables, and files. These docstrings can be very elaborate and span several pages. It should allow a new user to understand how to use it. Separate a class's methods by a single blank line.""" def somefunction(name): """Do something and return x. The summary line needs to fit on one line, end with a period, and have a newline after it."""Documenting Python, Docstring Example, Docstring Documentation, reStructuredText Docs
Debugging
- Examine error messages. Often, starting from the bottom makes it easier to understand.
- Make sure examples and inherited code work properly.
- Check (print) intermediate results.
-
Keep and compare old versions. You can do this by commenting out code (
cmd + /in Atom) or using a version control system like git.
Testing
Use unit testing to make sure all your functions work on their own.
# Test each function
assert function1(args) == answer
assert function2(args) == answer
for (args, answer) in test_cases:
try:
result = function(*args)
if result != answer:
else:
except AssertionError:
if answer = "AssertionError":
else:
Use the following to test program.py from the command line.
python -c "import program; program.test()"
Lesson 9: How to Solve Problems
Understanding the Problem
Problem is defined by possible inputs (set) and their relation to the desired outputs.
Solution: input -> procedure -> output
- What are the inputs?
- What is the set of valid inputs?
- How are the inputs represented?
- What are the edge cases?
- What are the outputs?
- Understand the relationship. Work through examples by hand.
-
Simple mechanical solution.
- Don't optimize prematurely. Simple and correct is more important.
- Develop incrementally and test as we go.
Programming Tips
- Build pseudocode.
- Use stubs to build helper functions.
- Account for edge cases.
Misc
People
- Admiral Grace Hopper - Wrote Cobalt and one of the first compilers.
- Ada Lovelace - Wrote the first computer program
- Alan Turing - Proved that a simple machine, Turing Machine, could simulate any other machine, using arithmetic, comparisons, procedures, and if statements.

